Compound 治理源码详解
这几天在学习CompoundDao治理,初看代码有些细节理解起来还是要费点功夫,写篇文章帮助大家理解
简述 Compound 治理
Compound 是一个去中心化借贷项目 ,他采用去中心化的治理机制(链上治理):Compound 项目的治理是完全去中心化的,COMP 持有者保持对协议的完全控制,因为只有通过 Compound 社区治理系统才能对该协议进行更改。Compound 的这种治理系统已成为行业标准之一,被 Uniswap、Gitcoin、PoolTogether 等其他大型项目采用。
Compound 治理源码分析
代码结构
首先我们需要梳理一下治理机制的大体过程:创建提案,成员委托投票,提案通过加入执行队列,等待宽限期,执行提案。
核心合约如下:
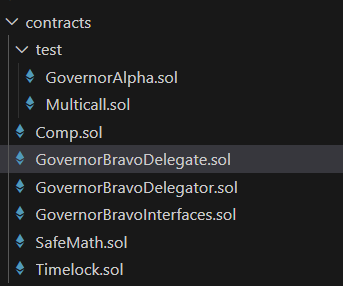
- Alpha合约是早期版本的治理合约。
- Comp是Token合约,实现了ERC20基本功能和代理以及票数统计功能。
- GovernorBravo是升级后的治理合约,和GovernorAlpha的功能大体类似,是一个可升级代理。
- GovernorBravoDelegate是实现合约。
- GovernorBravoDelegator是代理合约。
- GovernorBravoInterfaces是工具合约,包含其余合约所需实践,变量/常量,结构体,接口。
- Timelock是执行合约,控制提案入队,取消,执行。
升级功能
现在的Compound治理使用的是典型的代理升级模式,这意味着能轻松更新和扩展治理机制和功能。
合约代码分析
Comp合约
源码并未继承其他ERC20库,而是自己实现了Token基本功能。后面实践部分进行了继承,实现功能相同。
Checkpoint机制
在讲解token源码之前需要先了解在Compound治理中的一个核心机制:检查点机制
在每一次进行投票时,后面我们会发现实际上是将自己的权重(token数量)委托给其他地址时,会生成一个checkpoint记录当下的块num和权重,也就是vote数量.
这样做有什么意义呢?
我认为有两个:
- 防止重复计票:因为一个地址的票数是由其所拥有的token数量来统计的,但在对同一提案投票时,并不会消耗token,这就意味着可以无限次重复投票,并且用户会频繁的交易,每个时间点其token都在变化,如何在一个提案提出后,精准获取投票时间每个成员的票数,这就需要一个检查点来记录,下面会有一张图简单说明:
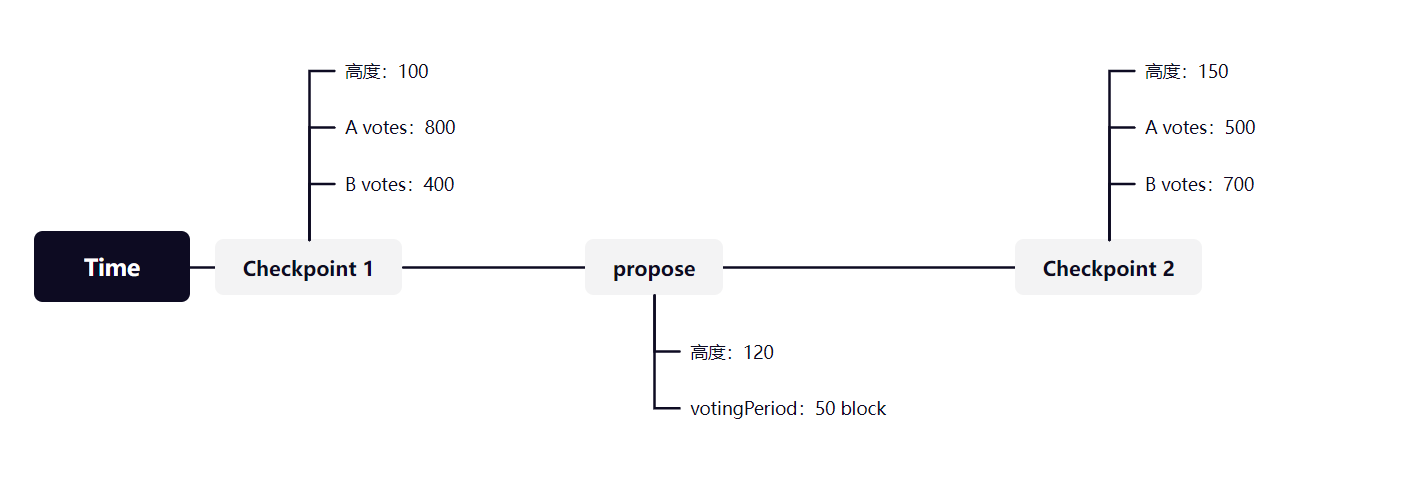 我们可以看到这里有两个检查点,一个在propose提出之前,一个在其之后,那么哪一个检查点的票数是属于propose的呢?
我们可以看到这里有两个检查点,一个在propose提出之前,一个在其之后,那么哪一个检查点的票数是属于propose的呢?
-
答案是 Checkpoint2,也就是说,一个提案被创建后,离他最近,且在其votingPeriod内的检查点所记录的票数就是这个提案的所得票数,我们从代码中也可以看出来:
治理合约中的投票函数:
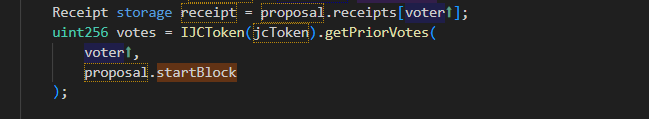 这是comp中的计票函数,在执行逻辑前会验证当前调用投票函数是是否在其投票时间内:
这是comp中的计票函数,在执行逻辑前会验证当前调用投票函数是是否在其投票时间内:
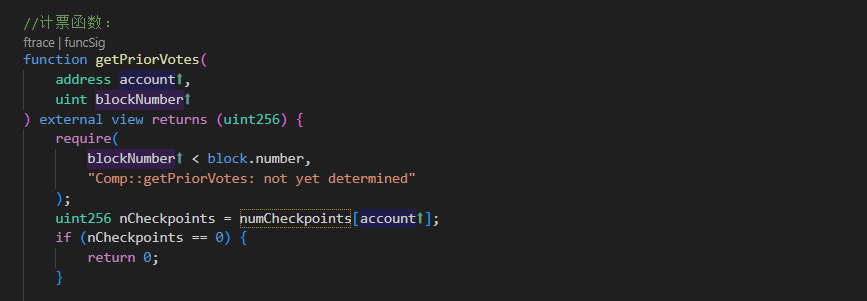
- 防止攻击:因为在启动投票的时候,我们一般会指定一个快照时间(checkpoint),而不是在投票人投票的瞬间去查询它的投票权重,防止有攻击者临时购买大量代币发起攻击.
说完了checkpoint,我们再来看看源码.除了基本的Token功能,Comp有如下核心功能:
状态变量
/// @notice A record of each accounts delegate
mapping (address => address) public delegates;
/// @notice A checkpoint for marking number of votes from a given block
struct Checkpoint {
uint32 fromBlock;
uint96 votes;
}
/// @notice A record of votes checkpoints for each account, by index
mapping (address => mapping (uint32 => Checkpoint)) public checkpoints;
/// @notice The number of checkpoints for each account
mapping (address => uint32) public numCheckpoints;- delegates:成员和委托地址的映射
- Checkpoint:检查点结构体,包含检查点所在的区块和对应的票数
- checkpoints:地址与其所拥有的检查点映射。
- numCheckpoints:每个地址对应的检查点数量。
核心函数
-
delegate()/_delegate():委托合约,也是将自己的token映射为vote的核心函数.这个函数涉及三个函数:
/** * @notice Delegate votes from `msg.sender` to `delegatee` * @param delegatee The address to delegate votes to */ function delegate(address delegatee) public { return _delegate(msg.sender, delegatee); }- _delegate():_将自己的票数(权重)委托给另一个地址(委托人),再调用moveDelegates()
function _delegate(address delegator, address delegatee) internal { address currentDelegate = delegates[delegator]; uint96 delegatorBalance = balances[delegator]; delegates[delegator] = delegatee; emit DelegateChanged(delegator, currentDelegate, delegatee); _moveDelegates(currentDelegate, delegatee, delegatorBalance); }- __moveDelegates():更新委托人和被委托人的权重/票数,调用writeCheckpoint();在处理的时候,要先从checkpoints查询上次更新后的投票权重RepOld,然后加/减本次的amount,再调用_writeCheckpoint写入map。
function _moveDelegates(address srcRep, address dstRep, uint96 amount) internal { if (srcRep != dstRep && amount > 0) { if (srcRep != address(0)) { uint32 srcRepNum = numCheckpoints[srcRep]; uint96 srcRepOld = srcRepNum > 0 ? checkpoints[srcRep][srcRepNum - 1].votes : 0; uint96 srcRepNew = sub96(srcRepOld, amount, "Comp::_moveVotes: vote amount underflows"); _writeCheckpoint(srcRep, srcRepNum, srcRepOld, srcRepNew); } if (dstRep != address(0)) { uint32 dstRepNum = numCheckpoints[dstRep]; uint96 dstRepOld = dstRepNum > 0 ? checkpoints[dstRep][dstRepNum - 1].votes : 0; uint96 dstRepNew = add96(dstRepOld, amount, "Comp::_moveVotes: vote amount overflows"); _writeCheckpoint(dstRep, dstRepNum, dstRepOld, dstRepNew); } }- _writeCheckpoint:为当前的委托人更新/增加checkpoint.
下面的_writeCheckpoint就是投票权重发生变化时会调用的函数。里面有一个if判断,如果if成立说明是同一个区块发生了多次投票权变更,那么直接以后一次的为准即可;如果if不成立则需要在map里增添一条记录,并把numCheckpoints增加1.
function _writeCheckpoint(address delegatee, uint32 nCheckpoints, uint96 oldVotes, uint96 newVotes) internal { uint32 blockNumber = safe32(block.number, "Comp::_writeCheckpoint: block number exceeds 32 bits"); if (nCheckpoints > 0 && checkpoints[delegatee][nCheckpoints - 1].fromBlock == blockNumber) { checkpoints[delegatee][nCheckpoints - 1].votes = newVotes; } else { checkpoints[delegatee][nCheckpoints] = Checkpoint(blockNumber, newVotes); numCheckpoints[delegatee] = nCheckpoints + 1; } emit DelegateVotesChanged(delegatee, oldVotes, newVotes); } -
getPriorVotes():被投票函数调用.寻找account在blockNumber内最近的checkpoint,这里的blockNumber是propose的startBlock,也就是开始投票的时间.
- checkpoints按照时间顺序记录了历史投票记录变更,如果我们把历史记录遍历一边,就可以确认它在某个区块的权重了。不过因为记录是有序的,所以我们不必线性查找,而是可以二分查找以提升效率。
function getPriorVotes(address account, uint blockNumber) public view returns (uint96) { require(blockNumber < block.number, "Comp::getPriorVotes: not yet determined"); uint32 nCheckpoints = numCheckpoints[account]; if (nCheckpoints == 0) { return 0; } // First check most recent balance if (checkpoints[account][nCheckpoints - 1].fromBlock <= blockNumber) { return checkpoints[account][nCheckpoints - 1].votes; } // Next check implicit zero balance if (checkpoints[account][0].fromBlock > blockNumber) { return 0; } uint32 lower = 0; uint32 upper = nCheckpoints - 1; while (upper > lower) { uint32 center = upper - (upper - lower) / 2; // ceil, avoiding overflow Checkpoint memory cp = checkpoints[account][center]; if (cp.fromBlock == blockNumber) { return cp.votes; } else if (cp.fromBlock < blockNumber) { lower = center; } else { upper = center - 1; } } return checkpoints[account][lower].votes; }
综上可以看出,comp合约的核心业务就是让持币者将自己的权重委托给委托人,同时设置对应的检查点.当委托人去投票时,根据其检查点获取委托人的权重(票数).如果还有些不懂也没关系,后面的部分会让你豁然开朗.
治理合约
前面说到现在的治理合约是可升级的,所以治理合约分为两个:代理合约和实现合约.
代理合约主要就了解一个通过fallback来调用代理合约逻辑.
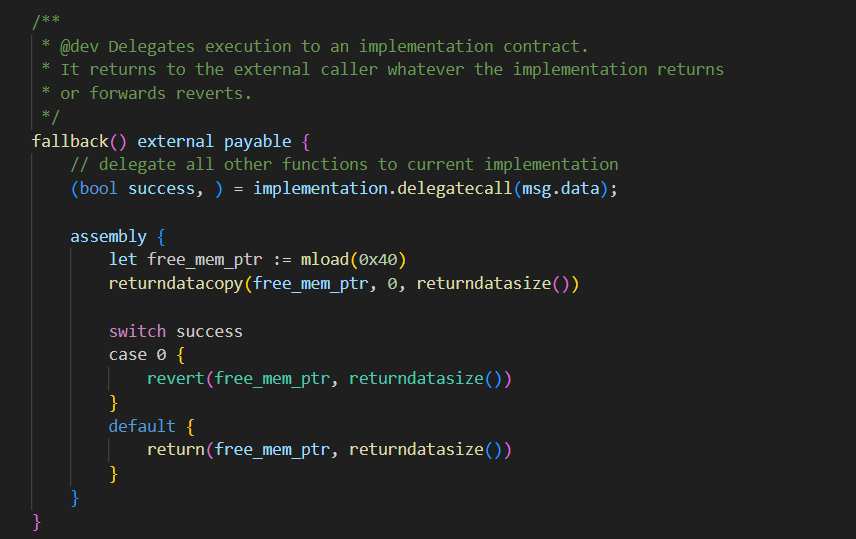 重点在于实现合约
重点在于实现合约
状态变量
首先,我们来看一下一个提案包含哪些属性:
struct Proposal {
/// @notice Unique id for looking up a proposal
uint id;
/// @notice Creator of the proposal
address proposer;
/// @notice The timestamp that the proposal will be available for execution, set once the vote succeeds
uint eta;
/// @notice the ordered list of target addresses for calls to be made
address[] targets;
/// @notice The ordered list of values (i.e. msg.value) to be passed to the calls to be made
uint[] values;
/// @notice The ordered list of function signatures to be called
string[] signatures;
/// @notice The ordered list of calldata to be passed to each call
bytes[] calldatas;
/// @notice The block at which voting begins: holders must delegate their votes prior to this block
uint startBlock;
/// @notice The block at which voting ends: votes must be cast prior to this block
uint endBlock;
/// @notice Current number of votes in favor of this proposal
uint forVotes;
/// @notice Current number of votes in opposition to this proposal
uint againstVotes;
/// @notice Current number of votes for abstaining for this proposal
uint abstainVotes;
/// @notice Flag marking whether the proposal has been canceled
bool canceled;
/// @notice Flag marking whether the proposal has been executed
bool executed;
/// @notice Receipts of ballots for the entire set of voters
mapping (address => Receipt) receipts;
}看起来很多,实际上确实很多,但并不难理解,我们只需要看注释就可以知道每个属性代表着什么,我在这解释几个难懂的:
- eta:提议可执行的时间
- targets:提议所要执行的合约
- startBlock/endBlock:开始投票/结束投票时间
- receipts:每个地址的投票情况的映射
其他的属性大多数看注释都能明白,主要解释几个特殊的
uint public votingDelay;
uint public votingPeriod;
uint public proposalThreshold;
TimelockInterface public timelock;
uint public constant quorumVotes = 400000e18; // 400,000 = 4% of Comp- votingDelay:在开始投票之前,有一段延迟时间,我称其为委托期
- votingPeriod:投票的时间
- proposalThreshold:发起提案的门槛(权重)
- timelock:时间锁,控制提案的各种执行
- quorumVotes:提案通过的门槛(超过一定票数就通过)
核心功能
发起提案
function propose(
address[] memory targets,
uint[] memory values,
string[] memory signatures,
bytes[] memory calldatas,
string memory description
) public returns (uint) {
return
proposeInternal(
msg.sender,
targets,
values,
signatures,
calldatas,
description
);
}
function proposeInternal(
address proposer,
address[] memory targets,
uint[] memory values,
string[] memory signatures,
bytes[] memory calldatas,
string memory description
) internal returns (uint) {
// Reject proposals before initiating as Governor
require(
initialProposalId != 0,
"GovernorBravo::proposeInternal: Governor Bravo not active"
);
// Allow addresses above proposal threshold and whitelisted addresses to propose
require(
comp.getPriorVotes(proposer, block.number - 1) >
proposalThreshold ||
isWhitelisted(proposer),
"GovernorBravo::proposeInternal: proposer votes below proposal threshold"
);
require(
targets.length == values.length &&
targets.length == signatures.length &&
targets.length == calldatas.length,
"GovernorBravo::proposeInternal: proposal function information arity mismatch"
);
require(
targets.length != 0,
"GovernorBravo::proposeInternal: must provide actions"
);
require(
targets.length <= proposalMaxOperations,
"GovernorBravo::proposeInternal: too many actions"
);
uint latestProposalId = latestProposalIds[proposer];
if (latestProposalId != 0) {
ProposalState proposersLatestProposalState = state(
latestProposalId
);
require(
proposersLatestProposalState != ProposalState.Active,
"GovernorBravo::proposeInternal: one live proposal per proposer, found an already active proposal"
);
require(
proposersLatestProposalState != ProposalState.Pending,
"GovernorBravo::proposeInternal: one live proposal per proposer, found an already pending proposal"
);
}
uint startBlock = block.number + votingDelay;
uint endBlock = startBlock + votingPeriod;
proposalCount++;
uint newProposalID = proposalCount;
Proposal storage newProposal = proposals[newProposalID];
// This should never happen but add a check in case.
require(
newProposal.id == 0,
"GovernorBravo::proposeInternal: ProposalID collision"
);
newProposal.id = newProposalID;
newProposal.proposer = proposer;
newProposal.eta = 0;
newProposal.targets = targets;
newProposal.values = values;
newProposal.signatures = signatures;
newProposal.calldatas = calldatas;
newProposal.startBlock = startBlock;
newProposal.endBlock = endBlock;
newProposal.forVotes = 0;
newProposal.againstVotes = 0;
newProposal.abstainVotes = 0;
newProposal.canceled = false;
newProposal.executed = false;
latestProposalIds[newProposal.proposer] = newProposal.id;
emit ProposalCreated(
newProposal.id,
proposer,
targets,
values,
signatures,
calldatas,
startBlock,
endBlock,
description
);
return newProposal.id;
}当要发起提案时,会进行一系列的判断,如判断上一个提案是否已经处理,提案的门槛是否达到(proposalThreshold)等。通过判定后,自增一个提案id,就将提案信息录入表中。
投票
投票的核心函数是castVoteInternal
三个参数:
- 投票人
- 提案id
- 反对或支持或中立:0,1,2
投票时,会先判断当前提案的状态(state方法),然后获取voter的票数(权重),这里就需要用之前说过getPriorVotes方法,传入voter和当前要进行投票提案的开始投票时间(proposal.startBlock)。获得了票数后,加到对应种类的票上,记录到提案中。到时候判断一个提案是否成功就是根据提案的三种票数(againstVotes,forVotes,abstainVotes)来判断的。
function _castVoteInternal(
address voter,
uint proposalId,
uint8 support
) internal returns (uint256) {
require(
state(proposalId) == ProposalState.Active,
"GovernorBravo::castVoteInternal: voting is closed"
);
require(
support <= 2,
"GovernorBravo::castVoteInternal: invalid vote type"
);
Proposal storage proposal = proposals[proposalId];
Receipt storage receipt = proposal.receipts[voter];
uint256 votes = IJCToken(jcToken).getPriorVotes(
voter,
proposal.startBlock
);
if (support == 0) {
proposal.againstVotes = proposal.againstVotes + votes;
} else if (support == 1) {
proposal.forVotes = proposal.forVotes + votes;
} else if (support == 2) {
proposal.abstainVotes = proposal.abstainVotes + votes;
}
receipt.hasVoted = true;
receipt.support = support;
receipt.votes = uint96(votes);
return votes;
}入队
通过的提案都会进入执行队列,但需要EOA主动调用
要将提案加入执行队列,需要判定当前提案的状态是否为success,这里用到了state方法,后面会讲。
获取提案可执行时间:加入队列的时间+宽限期(delay)
ps:宽限期是留时间让成员自行选择是否坚持新提案的共识,如果有异议可以选择退出或其他行为。
然后调用queueOrRevertInternal,这个方法也是调用的timelock合约的函数:
function queue(uint proposalId) external {
require(
state(proposalId) == ProposalState.Succeeded,
"GovernorBravo::queue: proposal can only be queued if it is succeeded"
);
Proposal storage proposal = proposals[proposalId];
uint eta = block.timestamp + timelock.delay();
for (uint i = 0; i < proposal.targets.length; i++) {
queueOrRevertInternal(
proposal.targets[i],
proposal.values[i],
proposal.signatures[i],
proposal.calldatas[i],
eta
);
}
proposal.eta = eta;
emit ProposalQueued(proposalId, eta);
}
function queueOrRevertInternal(
address target,
uint value,
string memory signature,
bytes memory data,
uint eta
) internal {
require(
!timelock.queuedTransactions(
keccak256(abi.encode(target, value, signature, data, eta))
),
"GovernorBravo::queueOrRevertInternal: identical proposal action already queued at eta"
);
timelock.queueTransaction(target, value, signature, data, eta);
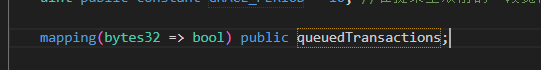
}这里是timelock的queueTransaction函数,主要作用就是将进入队列的提案的信息进行hash,添加到timelock的表中,以便对提案进行管理(取消,执行,去重):
function queueTransaction(address target, uint value, string memory signature, bytes memory data, uint eta) public returns (bytes32) {
require(msg.sender == admin, "Timelock::queueTransaction: Call must come from admin.");
require(eta >= getBlockTimestamp().add(delay), "Timelock::queueTransaction: Estimated execution block must satisfy delay.");
bytes32 txHash = keccak256(abi.encode(target, value, signature, data, eta));
queuedTransactions[txHash] = true;
emit QueueTransaction(txHash, target, value, signature, data, eta);
return txHash;
}状态
在治理合约中,我们全程都要维护提案的状态,通过提案的状态来判定是否进行对应的逻辑,例如上面我们在将提案加入到执行队列中时需要获取提案的状态是否是succeeded。
一个提案的状态如下:
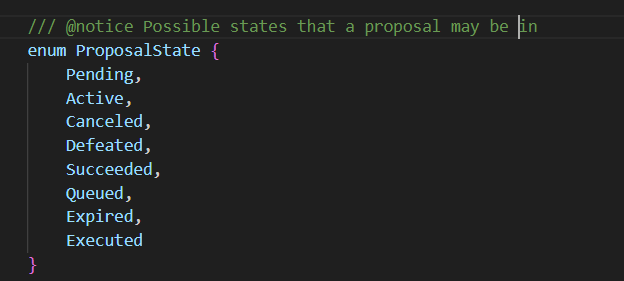
- Pending:提案处于委托期(等待成员将权重委托给委托地址,还不能投票)
- Active:提案处于投票期
- Canceled:提案已经被取消了
- Defeated:提案被驳回(未通过)
- Succeeded:提案成功(通过)
- Queued:提案在执行队列中等待执行(等待宽限期过)
- Expired:提案已经过期了
- Executed:提案已经被执行了
治理合约函数通过下面的state函数获取提案的状态进行下一步逻辑:
function state(uint proposalId) public view returns (ProposalState) {
require(
proposalCount >= proposalId && proposalId > initialProposalId,
"GovernorBravo::state: invalid proposal id"
);
Proposal storage proposal = proposals[proposalId];
if (proposal.canceled) {
return ProposalState.Canceled;
} else if (block.number <= proposal.startBlock) {
return ProposalState.Pending;
} else if (block.number <= proposal.endBlock) {
return ProposalState.Active;
} else if (
proposal.forVotes <= proposal.againstVotes ||
proposal.forVotes < quorumVotes
) {
return ProposalState.Defeated;
} else if (proposal.eta == 0) {
return ProposalState.Succeeded;
} else if (proposal.executed) {
return ProposalState.Executed;
} else if (block.timestamp >= proposal.eta + timelock.GRACE_PERIOD()) {
return ProposalState.Expired;
} else {
return ProposalState.Queued;
}
}执行
执行提案需要其状态为queued,
require(
state(proposalId) == ProposalState.Queued,
"GovernorBravo::execute: proposal can only be executed if it is queued"
);然后再调用timelock的执行函数executeTransaction执行提案中的动作和逻辑。
function execute(uint proposalId) external payable {
require(
state(proposalId) == ProposalState.Queued,
"GovernorBravo::execute: proposal can only be executed if it is queued"
);
Proposal storage proposal = proposals[proposalId];
proposal.executed = true;
for (uint i = 0; i < proposal.targets.length; i++) {
timelock.executeTransaction(
proposal.targets[i],
proposal.values[i],
proposal.signatures[i],
proposal.calldatas[i],
proposal.eta
);
}
emit ProposalExecuted(proposalId);
}这里是timelock函数的executeTransaction,通过对提案的相关属性进行哈希,然后通过这个哈希在queuedTransactions表中查找来验证是否是在队列中的提案。
require(queuedTransactions[txHash], "Timelock::executeTransaction: Transaction hasn't been queued.");然后用call的方式执行data中的逻辑。
function executeTransaction(address target, uint value, string memory signature, bytes memory data, uint eta) public payable returns (bytes memory) {
require(msg.sender == admin, "Timelock::executeTransaction: Call must come from admin.");
bytes32 txHash = keccak256(abi.encode(target, value, signature, data, eta));
require(queuedTransactions[txHash], "Timelock::executeTransaction: Transaction hasn't been queued.");
require(getBlockTimestamp() >= eta, "Timelock::executeTransaction: Transaction hasn't surpassed time lock.");
require(getBlockTimestamp() <= eta.add(GRACE_PERIOD), "Timelock::executeTransaction: Transaction is stale.");
queuedTransactions[txHash] = false;
bytes memory callData;
if (bytes(signature).length == 0) {
callData = data;
} else {
callData = abi.encodePacked(bytes4(keccak256(bytes(signature))), data);
}
// solium-disable-next-line security/no-call-value
(bool success, bytes memory returnData) = target.call{value: value}(callData);
require(success, "Timelock::executeTransaction: Transaction execution reverted.");
emit ExecuteTransaction(txHash, target, value, signature, data, eta);
return returnData;
}Timelock合约
时间锁合约,控制提案的执行,取消,入队。通过设置宽限期和GRACE_PERIOD来控制提案在规定时间内执行。
注意:时间锁是由admin管理的,只有admin指定的pendingAdmin能执行,一般pendingAdmin为治理合约。
address public admin;
address public pendingAdmin;
function acceptAdmin() public {
require(msg.sender == pendingAdmin, "Timelock::acceptAdmin: Call must come from pendingAdmin.");
admin = msg.sender;
pendingAdmin = address(0);
emit NewAdmin(admin);
}
function setPendingAdmin(address pendingAdmin_) public {
require(msg.sender == address(this), "Timelock::setPendingAdmin: Call must come from Timelock.");
pendingAdmin = pendingAdmin_;
emit NewPendingAdmin(pendingAdmin);
}核心的函数主要是三个:queueTransaction,cancelTransaction,executeTransaction
上面已经讲了两个,cancelTransaction代码如下:
function cancelTransaction(address target, uint value, string memory signature, bytes memory data, uint eta) public {
require(msg.sender == admin, "Timelock::cancelTransaction: Call must come from admin.");
bytes32 txHash = keccak256(abi.encode(target, value, signature, data, eta));
queuedTransactions[txHash] = false;
emit CancelTransaction(txHash, target, value, signature, data, eta);
}可以看到逻辑非常简单,就是更改表中的提案对应哈希的映射为false就完了。
到这,compound治理的核心逻辑就讲完了,当然源码还不止这些,但都是依附于这些核心逻辑所添加的应对各种应用场景的功能如:proposeBySig,castVoteBySig,castVoteWithReason等等,这里就不再赘述。
下一篇 我们根据上面的治理逻辑完成简单的,完整的提案执行过程。
我是Sanji,他们都叫我山鸡,在校大学生,web3小学生,有交流或Hackathon组队意向都可私信
个人微信:Z18382250961.
版权声明
本文仅代表作者观点,不代表区块链技术网立场。
本文系作者授权本站发表,未经许可,不得转载。
 区块链技术网
区块链技术网




发表评论:
◎欢迎参与讨论,请在这里发表您的看法、交流您的观点。